REMEMBER: OVARIAN CANCER DOES NOT SHOUT, IT WHISPERS!
Why are these FACTS important to you? – Ovarian cancer is typically portrayed as a “silent” killer, without much signs or symptoms until it is an advanced disease. – The sooner the cancer is detected and treated, the better a woman’s chance for recovery. Approximately 70% of women are diagnosed at late stage 3 or 4 of the disease . – Early detection can save lives and improve quality of life. Remember, AGAIN “ovarian cancer do not shout, it whispers”. 1. What are ovaries? 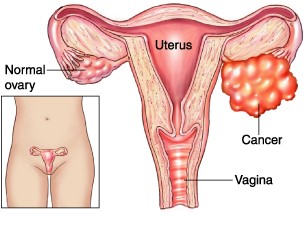 – Ovaries, also known as gonads, are female sexual organs that responsible in producing eggs and certain female hormones that regulate menstrual cycle and female sexuality. 2. What is ovarian cancer ? – Ovarian cancer is the cancer of the ovaries. – It commonly present in elderly women. – It can present early in women with certain genetic propensity (e.g. mutation in BRCA 1 and 2 gene) – Certain type of tumours also can present in childhood and adolescence. – The peak incidence is between 50- 59 years-old in Malaysia. 3. How common is ovarian cancer in Malaysia? – Ovarian cancer is the fourth most common cancer among Malaysian women – The incidence in 7.6 in 100,000 population. 4. What are the types of ovarian cancer?
– Ovaries, also known as gonads, are female sexual organs that responsible in producing eggs and certain female hormones that regulate menstrual cycle and female sexuality. 2. What is ovarian cancer ? – Ovarian cancer is the cancer of the ovaries. – It commonly present in elderly women. – It can present early in women with certain genetic propensity (e.g. mutation in BRCA 1 and 2 gene) – Certain type of tumours also can present in childhood and adolescence. – The peak incidence is between 50- 59 years-old in Malaysia. 3. How common is ovarian cancer in Malaysia? – Ovarian cancer is the fourth most common cancer among Malaysian women – The incidence in 7.6 in 100,000 population. 4. What are the types of ovarian cancer? 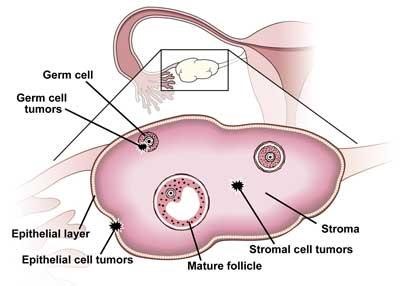 – There are 3 main types of ovarian cancer. – Epithelial ovarian cancer: most common type, 90% of cases, seen in older age group – Germ cell tumours – Sex cord stromal tumours, can present with menstrual irregularity and excessive hair growth 5. Who are at risk? – Woman of never having given birth – Woman who attain first menstrual bleeds before the age of 12 – Woman who attain menopause after the age of 55 – Increase in age – Woman who have family member with ovarian cancer – Woman who had breast cancer 6. What are the signs and symptoms? – The common presentation are: increase in abdomen size, bloating, sudden urge to urinate and pelvic pain. Some may also experience loss of appetite, loss of weight, nausea and vomiting. Mass may be felt in some. – It can also presents with acute abdominal pain when the tumour is twisted, rupture or bleed. – In rare cases, it can present with irregular menstrual bleeding before or after menopause, or excessive hair growth in young or elderly women. 7. What are the test for early detection in Ovarian Cancer? – There are no reliable early detection test available for the time being. – For women who are at high risks, a thorough pelvic examination by your physician with the combination of blood test (CA125) and ultrasound scan (transvaginal ultrasound) can be done to detect ovarian cancer. 8. What is the staging for Ovarian cancer? – Stage 1- Cancer limited to ovary. – Stage 2- Cancer within the organ surrounding the hip – Stage 3- Cancer within the abdominal cavity – Stage 4- Cancer spread to distant organ 9. How is Ovarian Cancer treated? – Woman with ovarian cancer will be sent for a keyhole surgery (laparoscopic staging) , to stage the severity and involvement of the cancer. Treatment of the ovarian cancer varies with the staging results. – After the cancer is confirmed, surgical removal of the cancer mass are often done. The removal of the surrounding organs which are affected by the cancer may be necessary as well. – Patient with advanced stage may require a chemotherapy and radiotherapy. 10. What are the outcome of the treatment? – 45% of the woman with ovarian cancer survive more than 5 years. Outcomes are better in those without spread of the cancer. Prepared by: Mak See Mun, Semester 9 Medical Student, International Medical University See Jie Siang, Semester 9 Medical Student, International Medical University Supervised : Dr Kavitha Nagandla, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, International Medical University
– There are 3 main types of ovarian cancer. – Epithelial ovarian cancer: most common type, 90% of cases, seen in older age group – Germ cell tumours – Sex cord stromal tumours, can present with menstrual irregularity and excessive hair growth 5. Who are at risk? – Woman of never having given birth – Woman who attain first menstrual bleeds before the age of 12 – Woman who attain menopause after the age of 55 – Increase in age – Woman who have family member with ovarian cancer – Woman who had breast cancer 6. What are the signs and symptoms? – The common presentation are: increase in abdomen size, bloating, sudden urge to urinate and pelvic pain. Some may also experience loss of appetite, loss of weight, nausea and vomiting. Mass may be felt in some. – It can also presents with acute abdominal pain when the tumour is twisted, rupture or bleed. – In rare cases, it can present with irregular menstrual bleeding before or after menopause, or excessive hair growth in young or elderly women. 7. What are the test for early detection in Ovarian Cancer? – There are no reliable early detection test available for the time being. – For women who are at high risks, a thorough pelvic examination by your physician with the combination of blood test (CA125) and ultrasound scan (transvaginal ultrasound) can be done to detect ovarian cancer. 8. What is the staging for Ovarian cancer? – Stage 1- Cancer limited to ovary. – Stage 2- Cancer within the organ surrounding the hip – Stage 3- Cancer within the abdominal cavity – Stage 4- Cancer spread to distant organ 9. How is Ovarian Cancer treated? – Woman with ovarian cancer will be sent for a keyhole surgery (laparoscopic staging) , to stage the severity and involvement of the cancer. Treatment of the ovarian cancer varies with the staging results. – After the cancer is confirmed, surgical removal of the cancer mass are often done. The removal of the surrounding organs which are affected by the cancer may be necessary as well. – Patient with advanced stage may require a chemotherapy and radiotherapy. 10. What are the outcome of the treatment? – 45% of the woman with ovarian cancer survive more than 5 years. Outcomes are better in those without spread of the cancer. Prepared by: Mak See Mun, Semester 9 Medical Student, International Medical University See Jie Siang, Semester 9 Medical Student, International Medical University Supervised : Dr Kavitha Nagandla, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, International Medical University