What is Pap smear screening? And why should you do the test? Pap smear test is a procedure that detects for changes in the cells of the cervix (neck of the womb). It detects whether there are any changes in the cervix that indicate cancer and if so, can be detected early and treated with complete cure at early stages. This is performed by taking a swab from the cervix. The swab is spread on the microscopic slide and looked for any abnormal cervical cancerous changes. This is not a diagnostic test, but a screening test. It does not provide 100% accurate results as ‘false positive ‘results (that is the test is positive in whom there is no abnormality) and ’false negative’ (that is the test is negative in the presence of abnormality) can occur. This indicates that in women with normal Pap smear can still develop cervical cancer. Who should undergo Pap smear screening and what is the screening schedule? Pap smear test is performed for women who are in 21 to 65 years and are sexually active and should be performed once a year. If two consecutive smear reports shows negative for abnormal cells, screening every three years is recommended.  How do I prepare myself prior to the test and how is it done? The ideal time to perform pap smear is when the women is not menstruating. The appropriate time is between 10 and 20 days after the first day of periods. Before the test, the women should avoid using vaginal douching or spermicidal creams or any medicines in the vagina. These may interfere with accurate interpretation of the results. This test will be performed by doctor or trained nurse in the clinic. The steps are as follows. – You will be placed on your back comfortably on examining table. A speculum will be inserted into the vagina. This speculum will open the vagina, so the cervix will come in vision. – A cotton swab will be introduced to clean any mucus that is covering the cervix. – The pap smear brush is a small cervical brush that is inserted into the cervical os and is twisted around on the cervix and this is the ectocervix sample and the cells are obtained by scraping the cells from the external cervix ( ecto- outside). A second sample is also collected from inside the cervix (endo-inside) – Both the samples are gently smeared on the glass slide with fixative and send to laboratory for evaluation.
How do I prepare myself prior to the test and how is it done? The ideal time to perform pap smear is when the women is not menstruating. The appropriate time is between 10 and 20 days after the first day of periods. Before the test, the women should avoid using vaginal douching or spermicidal creams or any medicines in the vagina. These may interfere with accurate interpretation of the results. This test will be performed by doctor or trained nurse in the clinic. The steps are as follows. – You will be placed on your back comfortably on examining table. A speculum will be inserted into the vagina. This speculum will open the vagina, so the cervix will come in vision. – A cotton swab will be introduced to clean any mucus that is covering the cervix. – The pap smear brush is a small cervical brush that is inserted into the cervical os and is twisted around on the cervix and this is the ectocervix sample and the cells are obtained by scraping the cells from the external cervix ( ecto- outside). A second sample is also collected from inside the cervix (endo-inside) – Both the samples are gently smeared on the glass slide with fixative and send to laboratory for evaluation.
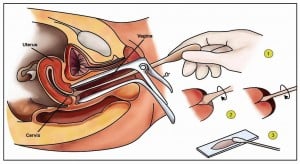 Fig 1: Steps in performing Pap smear test
Fig 1: Steps in performing Pap smear test
What do I expect from the results?
The results as reported are as follows: – Within normal limits – Unable to report due to inadequate sample – Inflammatory smear Abnormal results All the Pap smear abnormal results are based on medical terminology system referred as ‘The Bethesda System’. The term intraepithelial means that the surface layers of the cervical cells are affected. The term lesion refers that there is abnormal tissue. The reporting of abnormal Pap smears reported in the Bethesda Systems includes:
- LSIL: This abbreviation refers to low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.
- HSIL: This abbreviation refers to high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.
- ASC-US: This refers to atypical squamous cells of unknown significance (squamous cells refers to thin flat cells that are lining the surface of the cells.)
What happens if my smear is abnormal? ASC-US: This refers to mildest of abnormality refers to changes in the cervical cells that appear abnormal, but not cancer. This may be caused by human papilloma virus and as it is undetermined, the lesion disappears spontaneously. Hence the need to repeat pap smear in 6 months LSIL: This low grade refers to serious abnormality that needs immediate investigation. This is by undergoing colposcopy. It is estimated that 15-30 % of women with this abnormality will have some serious underlying problem in the cervix. However there is still possibility that LSIL may spontaneously return to normal without treatment. HSIL: This is a more serious abnormality as these women have 70-75% chance of progressing to cancer. What is colposcopy? This is the procedure that allows to take a closer look of the cervix. This apparatus has a magnifying glass that allows the entire cervix. The cervix is cleaned and soaked with 3 % acetic acid that allows abnormal changes to be clearly visible and are called as aceto-white areas. A biopsy will then be taken from these abnormal areas that will confirm whether there is cancer or not. What are the treatments available for abnormal pap smear results? The treatment options available are large loop excision of transformation zone (LEETZ), cone biopsy, cryo-cauterization and laser therapy. All these treatments involve removing the abnormal cervical changes and are associated with success rate of approximately 97%. Prepared by: Dr Nagandla Kavitha, Senior Lecturer, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Clinical School Seremban, International Medical University Yee Sze Howe, Semester 9 Student, International Medical University Santhi Asookumaran, Academic Services, Clinical School Seremban, International Medical University








