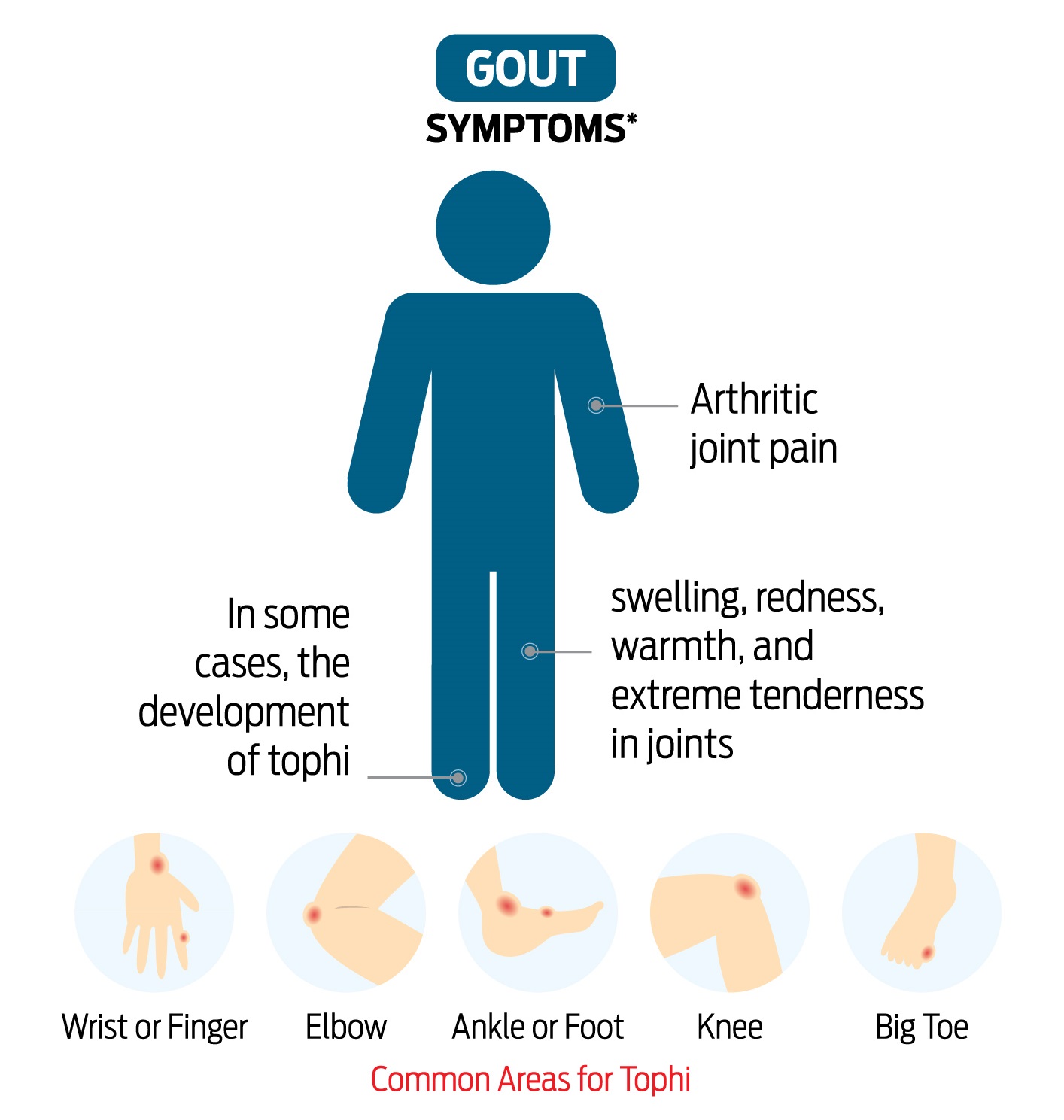
The Greek philosopher-physician Hippocrates called gout the “arthritis of the rich.” However, the notion that it is only a ‘rich man’s disease’ is untrue. Dr Benjamin Cheah, Rheumatologist, at IMU Healthcare helps demystify the disease, as well as shed light on rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which may also be present with joint pains. What is gout? Gout is a type of arthritis and is classified as a crystal-induced arthropathy. It is an inflammatory disease that happens when you have excessive uric acid in your body. When there is too much of it circulating in your bloodstream, it can be deposited as monosodium urate crystals in your joints. Usually, uric acid is excreted from the body through the kidneys. What are the signs and symptoms of gout? When crystals are deposited in and around your joints, you will experience swelling, redness and pain. This is due to inflammation. The joints that are commonly affected are the toes, ankles, knees and fingers. There is usually a precipitating event, for example a diet rich in red meat or seafood prior to the onset of pain.
Who is at risk of developing gout? There are several factors to consider. Firstly, doctors have noted that gout is more common in men than in women and children. Your genetics will also play a part. Studies have shown that between 20-80 percent of people afflicted with gout tend to have a family history where gout has been prevalent. Being overweight may increase your risk of contracting gout. This is usually associated with a condition called metabolic syndrome. Among the components of this is hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity and high uric acid levels. Heavy drinkers of alcohol might be at greater risk of developing gout because drinking too much alcohol prevents the body from removing the excess uric acid. You may also increase your chances of developing gout if you consume an excessive amount of food that can cause a build-up of uric acid. These foods include red meat, seafood and offal. An underactive thyroid, termed hypothyroidism, can also put you at increased risk of gout. How do doctors diagnose gout? Doctors extract a small amount of synovial fluid from your joint. The fluid is then analysed for the presence of monosodium urate crystals. The presence of these crystals in the synovial fluid is confirmatory of gout. How can gout be treated? Dietary restrictions is important. One should avoid food high in purine content, for example, red meat , seafood and offal. Alcohol and soft drinks should also be avoided. Your doctors will then prescribe you with medications to control the inflammation and pain. Among the medications commonly used are colchicine and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Steroids may sometimes be used. Medications that lower your uric acid, for example allopurinol, is given after the acute attack has subsided. Lowering the uric acid level will help reduce the frequency and severity of the attacks. What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)? Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease causing inflammation of the joints. The body attacks its own tissues much like how it attacks foreign bodies or bacteria when they invade our tissues. With RA, the body attacks its tissues in the synovial joints, which are the joints that cushion the impact of everyday movement. It can affect any synovial joints of the body. As a result of the inflammation, affected joints become stiff, swollen and painful. RA can cause irreversible damage to the joints. This can be disabling by severely limiting a person’s range of movement. RA is a systemic disease, which means it can affect other parts of the body, even the organs. There are termed extra-articular manifestations. Among them are the eyes and lungs. RA is treatable but not curable. The cause of RA is still unknown. It is likely a combination of genetics and the environment. There are some known triggers of RA. Among them is tobacco smoking. How is rheumatoid arthritis treated? Starting treatment early is important to avoid permanent joint damage. Among the medications used are steroids, disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic medications. They are very often used in combination. They will help reduce the inflammation and pain. More importantly, it can help prevent the onset of permanent joint damage. It is important to discuss the many treatment options with your doctor. What does a rheumatologist do? A rheumatologist is a medical professional who specialises in the area of detection/diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases. Rheumatic diseases refer to conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system and those related to autoimmunity. These conditions commonly affect the joints, bones and muscles causing pain, swelling or deformity. A patient can be referred to a rheumatologist if the joint or muscle pain is not resolving. The rheumatologist will then do a careful assessment which involves a thorough history taking and physical examination. He may then order some tests to help in the diagnosis. A treatment plan can then be formulated. SOURCES: http://www.arthritis.org/living-with-arthritis/tools-resources/expert-q-a/gout-questions/arthritis-or-gout.php http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/Gout/Pages/Introduction.aspx https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/magazine/issues/winter12/articles/winter12pg20.html http://www.medicinenet.com/gout_quiz/faq.htm http://www.healthline.com/health-slideshow/rheumatoid-arthritis-vs-gout http://www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Patient-Caregiver/Health-Care-Team/What-is-a-Rheumatologist This article is brought to you by IMU Healthcare.


Real informative and great complex body part of articles, now that’s user friendly (:.
Real informative and great complex body part of articles, now that’s user friendly (:.
Real informative and great complex body part of articles, now that’s user friendly (:.
Real informative and great complex body part of articles, now that’s user friendly (:.
I suffer from gout and take montmorency tart cherry juice every day as you mention. There is also turmeric for gout as well which has been found in studies to help reduce inflammation and uric acid levels due to its compound curcumin. It needs to be paired with piperine for added absorbability.
I suffer from gout and take montmorency tart cherry juice every day as you mention. There is also turmeric for gout as well which has been found in studies to help reduce inflammation and uric acid levels due to its compound curcumin. It needs to be paired with piperine for added absorbability.
I suffer from gout and take montmorency tart cherry juice every day as you mention. There is also turmeric for gout as well which has been found in studies to help reduce inflammation and uric acid levels due to its compound curcumin. It needs to be paired with piperine for added absorbability.
I suffer from gout and take montmorency tart cherry juice every day as you mention. There is also turmeric for gout as well which has been found in studies to help reduce inflammation and uric acid levels due to its compound curcumin. It needs to be paired with piperine for added absorbability.